目錄
- 前言
- while 的使用案例
- 1. 循環(huán)輸出1-10的數字
- 2. 使用while讀文件并打印文件內容
- 3. 輸出兩數相乘的效果(如下圖)
- 總結
前言
上文我們討論了for循環(huán)的使用����,在有限循環(huán)里,我們使用for循環(huán)是很方便的一件事情���,今天我們來探討下while循環(huán)
while循環(huán)語句的語法分析
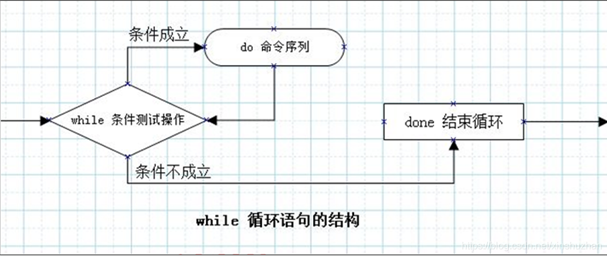
語法格式一:
語法格式二:
while read line
do
操作
done file
通過read命令每次讀取一行文件�,文件內容有多少行����,while循環(huán)多少次
注意:只有表達式為真,do和done之間的語句才會執(zhí)行�����,表達式為假時,結束循環(huán)(即條件成立就一直執(zhí)行循環(huán))
例如:
while true ;do
echo 'helloword'
done
while 的使用案例
1. 循環(huán)輸出1-10的數字
#!/bin/bash
num=1
while [ $num -le 10 ]
do
echo $num
num=$(( $num + 1 ))
done
2. 使用while讀文件并打印文件內容
用法一:
while read line
do
echo $line
done ./a.txt
用法二:
cat ./a.txt|
while read line
do
echo $line
done
for實現的讀取文件并著行打印
#!/bin/bash
content=$(cat ./a.txt)
for i in $content
do
echo $i
done
3. 輸出兩數相乘的效果(如下圖)
此處感謝 @一只小小白丶 的建議���,因為大多數人看到等號就會想到兩邊相等�,這符合我們的教育習慣���。
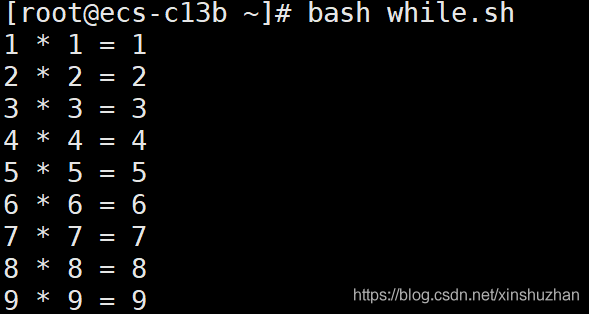
如果要實現圖中效果可以按照如下方式做:
#!/bin/bash
num=1
while [ $num -lt 10 ]
do
sum=$(( $num * $num))
echo "$num * $num = $num"
((num++))
done
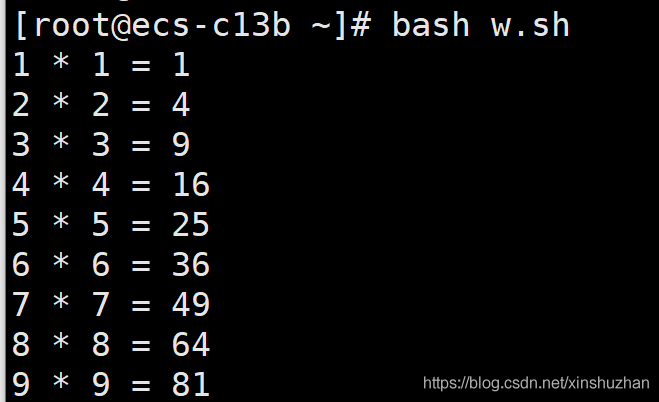
當然大多數人習慣了讓等式兩邊必須相等����,不相等看上去別扭���,這也是義務教育的結果�����,也可以稍微改一下:
#!/bin/bash
num=1
while [ $num -lt 10 ]
do
sum=$(( $num * $num))
echo "$num * $num = $sum"
((num++))
done
這樣輸出的結果符合大多數人的數學習慣:
創(chuàng)建指定文件里的用戶
指定文件 name.txt 里面包含 zhangsan lisi wangwu
name.txt 如下:
[root@ecs-c13b ~]# cat name.txt
zhangsan
lisi
wangwu
從name.txt里面遍歷用戶名并創(chuàng)建用戶
#!/bin/bash
for name in `cat /root/name.txt`
#for name in $(cat /root/a.txt)
do
id $name > /dev/null
if [ $? -ne 0 ];then
useradd $name
echo "123456" |passwd --stdin $name > /dev/null
echo "user $name created"
else
echo "user $name is exist"
fi
done
總結
到目前為止����,for-while-if-case����,這四個常用的控制語句我們都已經探討過了,接下來就是大量練習和綜合應用的時候�,操練起來把��。
到此這篇關于shell腳本實戰(zhàn)-while循環(huán)語句的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關shell -while循環(huán)內容請搜索腳本之家以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大家以后多多支持腳本之家�!
您可能感興趣的文章:- 監(jiān)控MySQL主從狀態(tài)的shell腳本
- shell腳本使用兩個橫杠接收外部參數的方法
- 使用Shell腳本如何啟動/停止Java的jar程序
- Shell中使用grep���、sed正則提取和替換字符串
- Shell eval通過變量獲取環(huán)境變量的方法實現
- shell腳本--sed的用法詳解
- linux shell中 if else以及大于、小于�、等于邏輯表達式介紹
- Linux中執(zhí)行shell腳本的4種方法總結
- 一個不錯的shell 腳本教程 入門級
- Shell字符串比較相等、不相等方法小結
- python中執(zhí)行shell命令的幾個方法小結
- 分享一個可以通過命令簡寫執(zhí)行對應命令的Shell腳本