上一章節(jié)介紹了PySide2的安裝以及如何去啟動程序進行頁面設計����,并且將工具集成到pycharm的擴展工具中去,有2個地方寫的不對�����,用的是pyuic工具����,需要改一下,改成pyside2-uic.exe���。具體改動點:
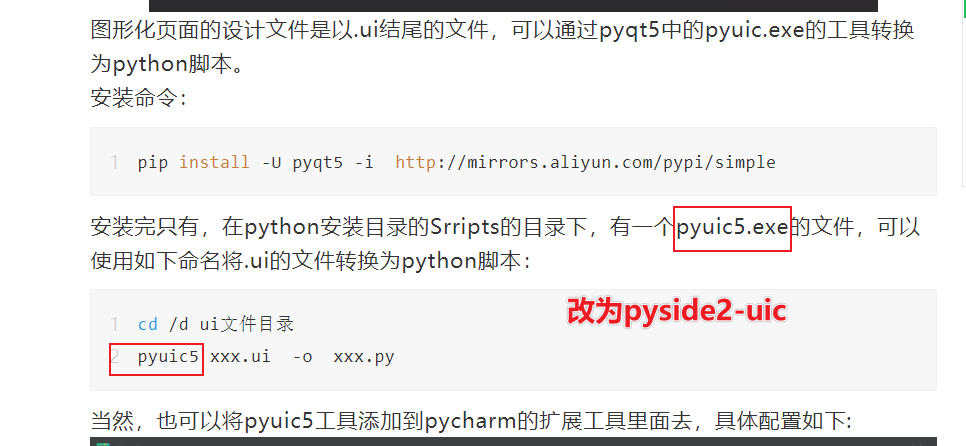
pycharm擴展工具中的配置也需要調整一下:

上一篇的配置寫的是pyqt5的配置�����,這里主要采用PySide2進行學習���。
修改為正確的配置后����,鼠標選中ui文件����,右鍵選擇擴展工具中的pyside2-uic就可以轉換為python腳本。
先看一下我畫的一個簡單的GUI頁面:
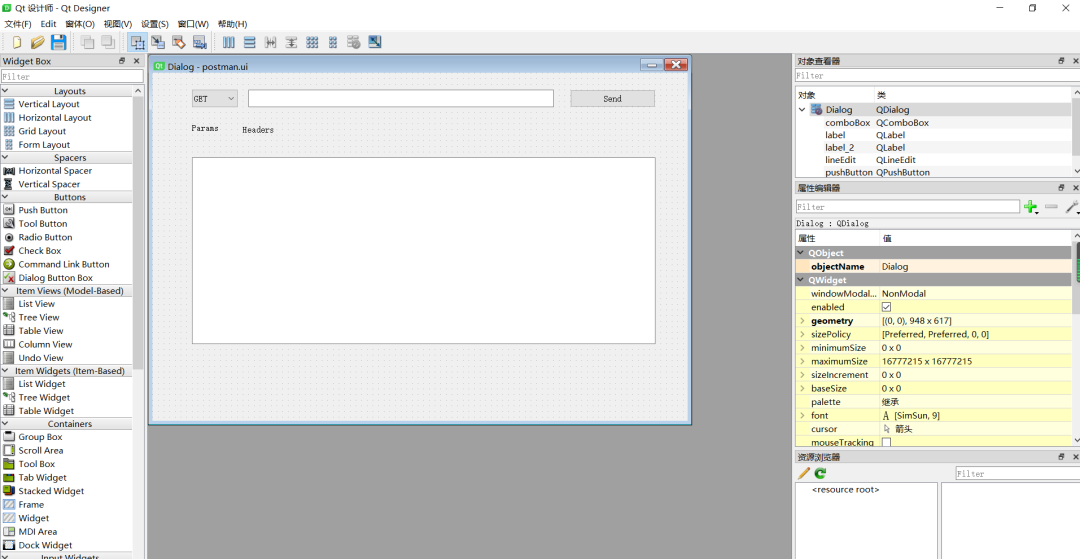
保存頁面文件后�����,后綴是.ui的格式�����,用文本文件打開的話�����,內容是xml格式的:
postman.ui源碼:
?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
ui version="4.0">
class>Dialog/class>
widget class="QDialog" name="Dialog">
property name="geometry">
rect>
x>0/x>
y>0/y>
width>948/width>
height>617/height>
/rect>
/property>
property name="windowTitle">
string>Dialog/string>
/property>
widget class="QComboBox" name="comboBox">
property name="geometry">
rect>
x>70/x>
y>30/y>
width>81/width>
height>31/height>
/rect>
/property>
item>
property name="text">
string>GET/string>
/property>
/item>
item>
property name="text">
string>POST/string>
/property>
/item>
/widget>
widget class="QLineEdit" name="lineEdit">
property name="geometry">
rect>
x>170/x>
y>30/y>
width>541/width>
height>31/height>
/rect>
/property>
/widget>
widget class="QPushButton" name="pushButton">
property name="geometry">
rect>
x>740/x>
y>30/y>
width>151/width>
height>31/height>
/rect>
/property>
property name="text">
string>Send/string>
/property>
/widget>
widget class="QLabel" name="label">
property name="geometry">
rect>
x>70/x>
y>90/y>
width>72/width>
height>15/height>
/rect>
/property>
property name="text">
string>Params/string>
/property>
/widget>
widget class="QLabel" name="label_2">
property name="geometry">
rect>
x>160/x>
y>90/y>
width>121/width>
height>21/height>
/rect>
/property>
property name="text">
string>Headers/string>
/property>
/widget>
widget class="QTextEdit" name="textEdit">
property name="geometry">
rect>
x>70/x>
y>150/y>
width>821/width>
height>331/height>
/rect>
/property>
/widget>
/widget>
resources/>
connections/>
/ui>
轉換之后的python腳本:postman.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
################################################################################
## Form generated from reading UI file 'postman.ui'
##
## Created by: Qt User Interface Compiler version 5.15.2
##
## WARNING! All changes made in this file will be lost when recompiling UI file!
################################################################################
from PySide2.QtCore import *
from PySide2.QtGui import *
from PySide2.QtWidgets import *
class Ui_Dialog(object):
def setupUi(self, Dialog):
if not Dialog.objectName():
Dialog.setObjectName(u"Dialog")
Dialog.resize(948, 617)
self.comboBox = QComboBox(Dialog)
self.comboBox.addItem("")
self.comboBox.addItem("")
self.comboBox.setObjectName(u"comboBox")
self.comboBox.setGeometry(QRect(70, 30, 81, 31))
self.lineEdit = QLineEdit(Dialog)
self.lineEdit.setObjectName(u"lineEdit")
self.lineEdit.setGeometry(QRect(170, 30, 541, 31))
self.pushButton = QPushButton(Dialog)
self.pushButton.setObjectName(u"pushButton")
self.pushButton.setGeometry(QRect(740, 30, 151, 31))
self.label = QLabel(Dialog)
self.label.setObjectName(u"label")
self.label.setGeometry(QRect(70, 90, 72, 15))
self.label_2 = QLabel(Dialog)
self.label_2.setObjectName(u"label_2")
self.label_2.setGeometry(QRect(160, 90, 121, 21))
self.textEdit = QTextEdit(Dialog)
self.textEdit.setObjectName(u"textEdit")
self.textEdit.setGeometry(QRect(70, 150, 821, 331))
self.retranslateUi(Dialog)
QMetaObject.connectSlotsByName(Dialog)
# setupUi
def retranslateUi(self, Dialog):
Dialog.setWindowTitle(QCoreApplication.translate("Dialog", u"Dialog", None))
self.comboBox.setItemText(0, QCoreApplication.translate("Dialog", u"GET", None))
self.comboBox.setItemText(1, QCoreApplication.translate("Dialog", u"POST", None))
self.pushButton.setText(QCoreApplication.translate("Dialog", u"Send", None))
self.label.setText(QCoreApplication.translate("Dialog", u"Params", None))
self.label_2.setText(QCoreApplication.translate("Dialog", u"Headers", None))
# retranslateUi
單單有以上兩個腳本是無法運行的,還需要單獨再寫幾行代碼來加載頁面窗口進行展示:
run_postman.py:
import sys
from PySide2.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow
from postman import Ui_Dialog
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 創(chuàng)建一個Application對象
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
# 創(chuàng)建一個窗體對象
MainWindow = QMainWindow()
ui = Ui_Dialog()
ui.setupUi(MainWindow)
# 設置窗口顯示
MainWindow.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
運行后的效果如下圖所示:
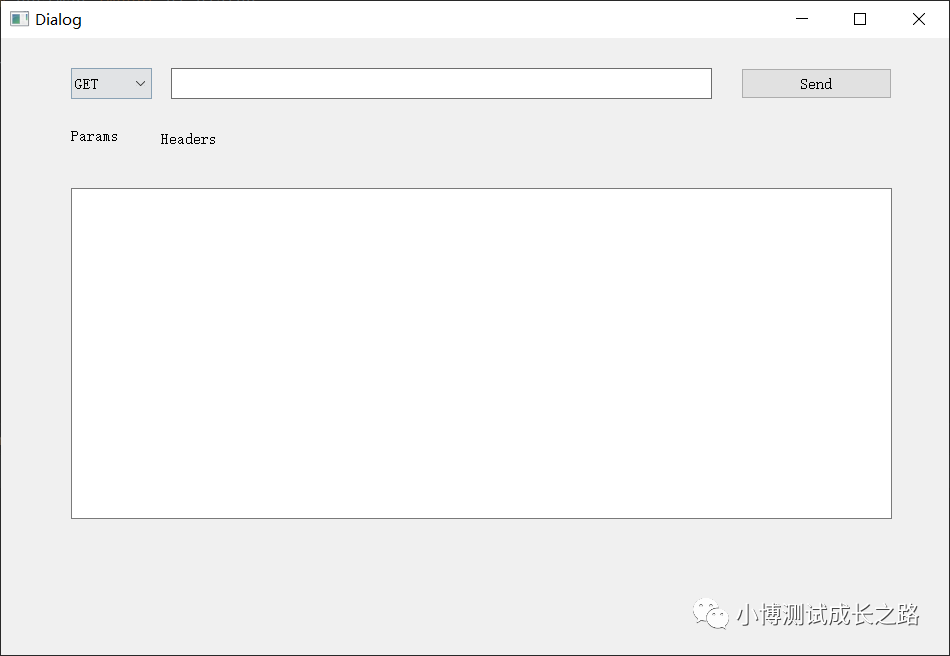
大家感興趣的話�����,可以根據自己的喜好去調整頁面設計�����,實現(xiàn)自己的測試小工具�。
到此這篇關于Python運行第一個PySide2的窗體程序的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關Python運行第一個PySide2的窗體程序內容請搜索腳本之家以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大家以后多多支持腳本之家����!
您可能感興趣的文章:- python入門課程第二講之怎么運行Python
- python運行加速的幾種方式
- Python命令行運行文件的實例方法
- python腳本打包后無法運行exe文件的解決方案
- 沒有安裝Python的電腦運行Python代碼教程